By 2027, 376.89 million users are expected to be added into the Neobanking industry. The transaction value in the Neobanking segment is expected to reach $4.53 trillion by 2023. The user penetration is expected to be 3.3% in 2023, rising to 4.8% by 2027. With a CAGR of 18.25% between 2023 to 2027, the total transaction value of Neobanks will reach around US$8.86tn in 2027. Countries like Ireland, Luxembourg, UK, Denmark and Brazil are going to be the top markets when it comes to user penetration in 2023 for Neobanks.
Table of contents
|
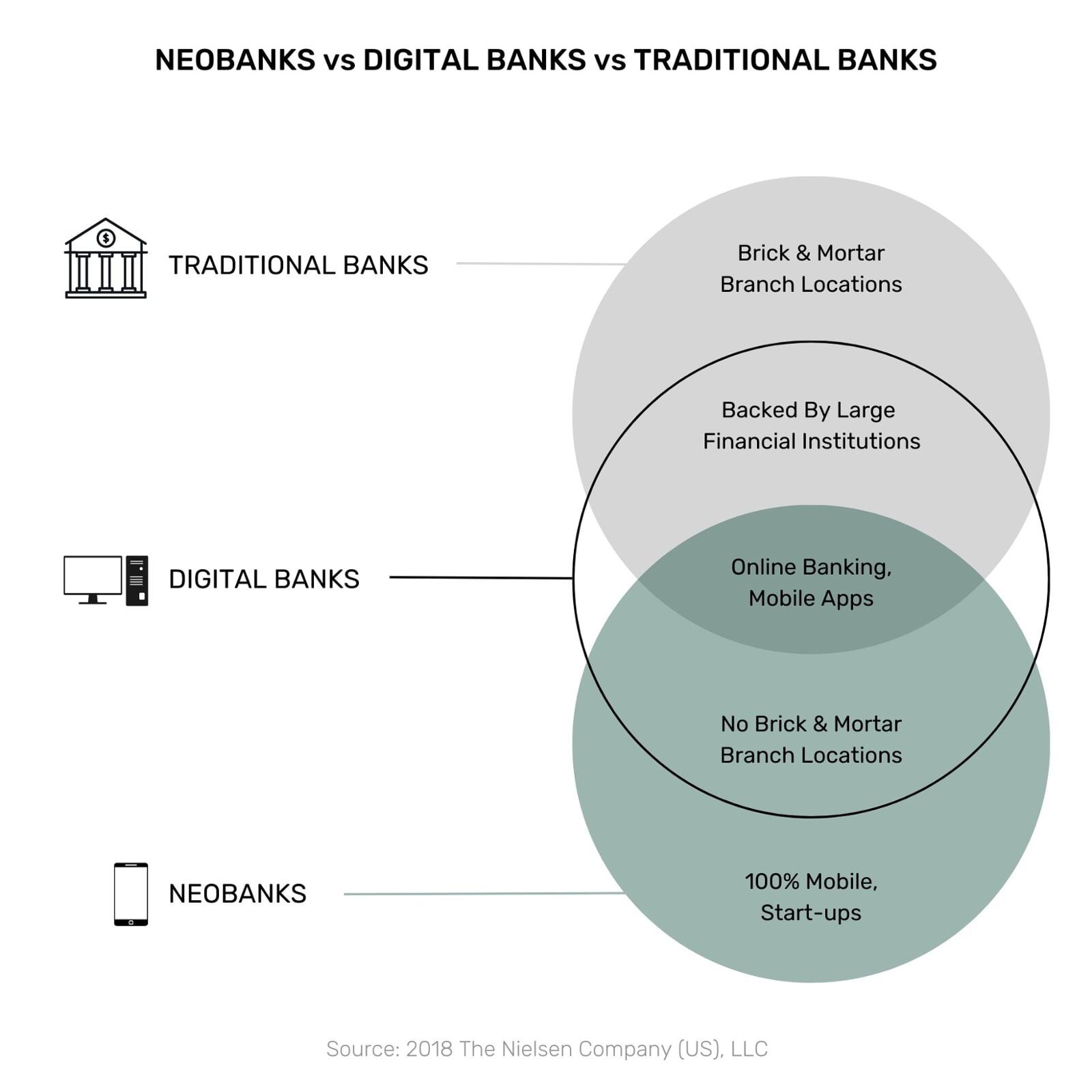
What are Neobanks?
A neobank is a type of digital bank that operates primarily online and through mobile apps, offering banking services such as account opening, money transfers, and debit card usage without the need for a physical branch network. They often target specific demographics, such as millennials or small businesses, and may offer features such as budgeting tools or cashback rewards.
Source: 2018 The Nielsen Company (US). LLC
What are the differences between a Neobank and a conventional bank?
Neobanks typically offer a similar range of financial products and services as traditional banks, such as checking and savings accounts, credit cards, and loans. However, there are several key differences between neobanks and conventional banks:
Which are the biggest Neobanks globally?
Note that this list is not exhaustive and the "biggest" neobanks may vary depending on factors such as assets under management, customer base, and funding.
What makes Neobanks so popular?
Neobanks have become popular for a number of reasons:
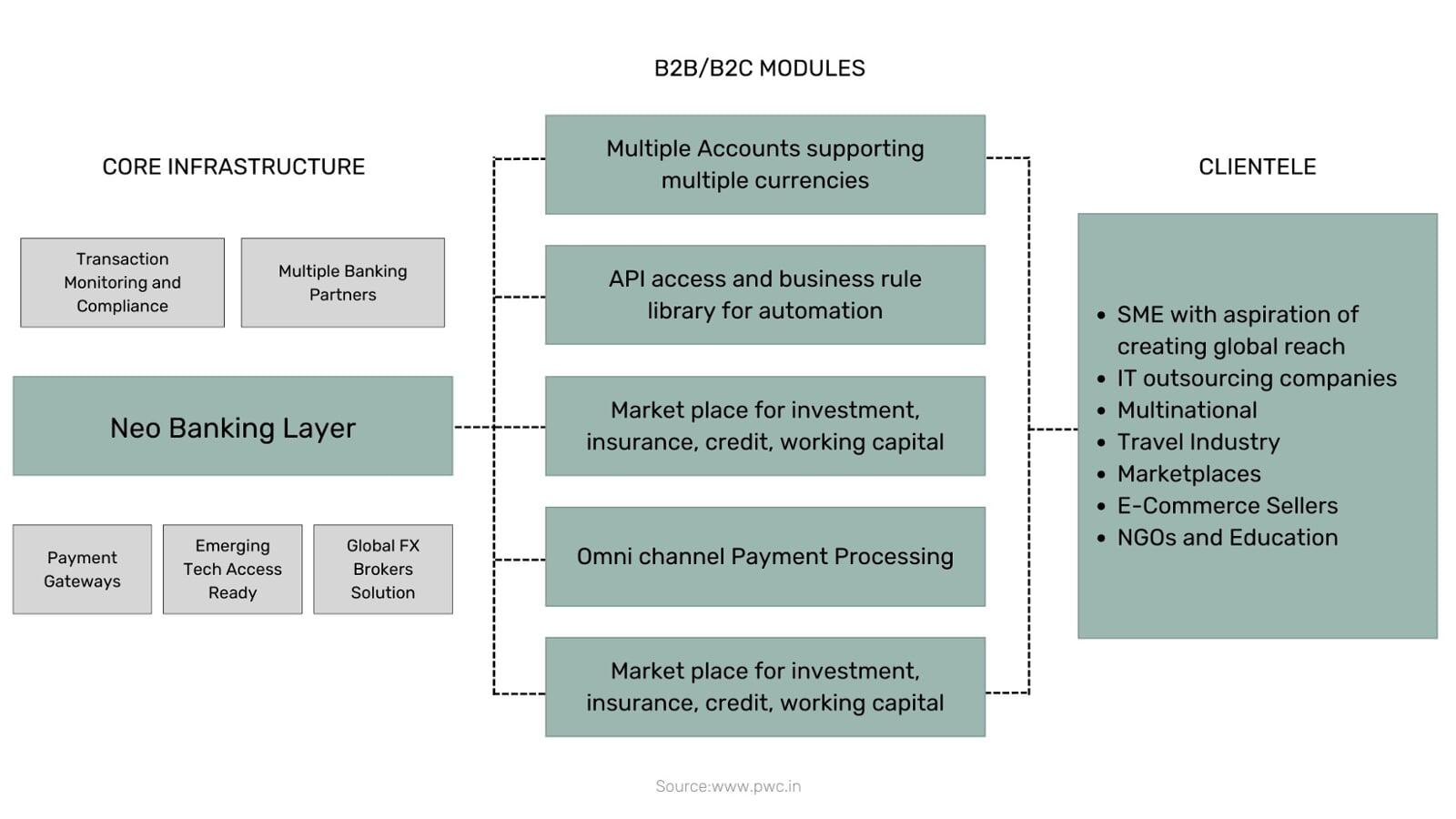
The current Neobank business models
Historically, neobanks have launched with a few classic features, such as low-cost FX and international money transfers (Revolut), fee-free credit cards (Nubank), and business accounts (Tide), and gradually evolved the proposition to include a broader range of services. The German neobank N26 and Revolut have a different approach, the ultimate goal is to build a multi-country, full-service digital bank that offers current accounts, lending, insurance, and investments.
Source: www.pwc.in
What advantage do Neobanks have over traditional banks?
Neobanks are able to differentiate themselves and gain an advantage over traditional banks in the following ways;
Factors that are hampering the profitability of Neobanks
These are some of the factors affecting the financial growth of the neobanks;
How Neobanks can leverage cross-border payments to increase their revenue growth?
It will be critical for both newcomers and existing players in the neobank space to identify their customers' pain points and devise innovative solutions to those problems. One wise strategy would be to carve out a niche by focusing on smaller segments of the population or offer most competitive options in one particular business segment, like cross-border payments.
Examples of Neobanks leveraging cross-border payments for business growth
One example of a neobank leveraging cross-border payments for business growth is Revolut. Revolut, a neobank based in the UK, has built a platform for cross-border payments that utilizes local bank transfers in different countries. This allows Revolut to offer more competitive exchange rates and lower fees compared to traditional banks. Revolut also offers a wide range of features for businesses, such as virtual and physical debit cards, expense management, and multi-currency accounts. By offering these services, Revolut has been able to attract small businesses and freelancers as customers, which has helped it to grow its customer base.
What cross-border payment strategies can Neobanks use to increase their revenue?
Neobanks can use the following cross-border payment strategies to improve their revenue;
- Offering competitive exchange rates and low fees for international transactions.
- Providing a seamless and user-friendly experience for customers.
- Partnering with other companies or payment providers that specialize in cross-border payments to offer a wider range of options. Neobanks can access financial products and services that are currently unavailable to them due to regulations by leveraging existing solutions and networks within the fintech ecosystem.
- Targeting specific markets or demographics with high demand for cross-border payments.
- Leveraging technology such as blockchain to facilitate cross-border payments and reduce costs.
- Creating a loyalty program for frequent cross-border payments and offering rewards for usage.
- Offering additional services such as foreign currency accounts, remittance, and global money transfers.
- Positioning the company as a one-stop-shop for all cross-border payments needs.
- Creating partnerships with other fintechs and financial institutions to expand services and offer more options to customers
- Investing in marketing and advertising campaigns to raise awareness of the neobank's cross-border payment capabilities.
Conclusion
The cross-border payments ecosystem is changing. The neobanks getting ahead are the neobanks with established client bases collaborating with cross-border payment solution providers who offer tailored products and go-to-market strategies. This is a fantastic opportunity for neobanks to gain international market share.
To acquire the platform, book a demo with the Fable Fintech cross-border platform experts;
